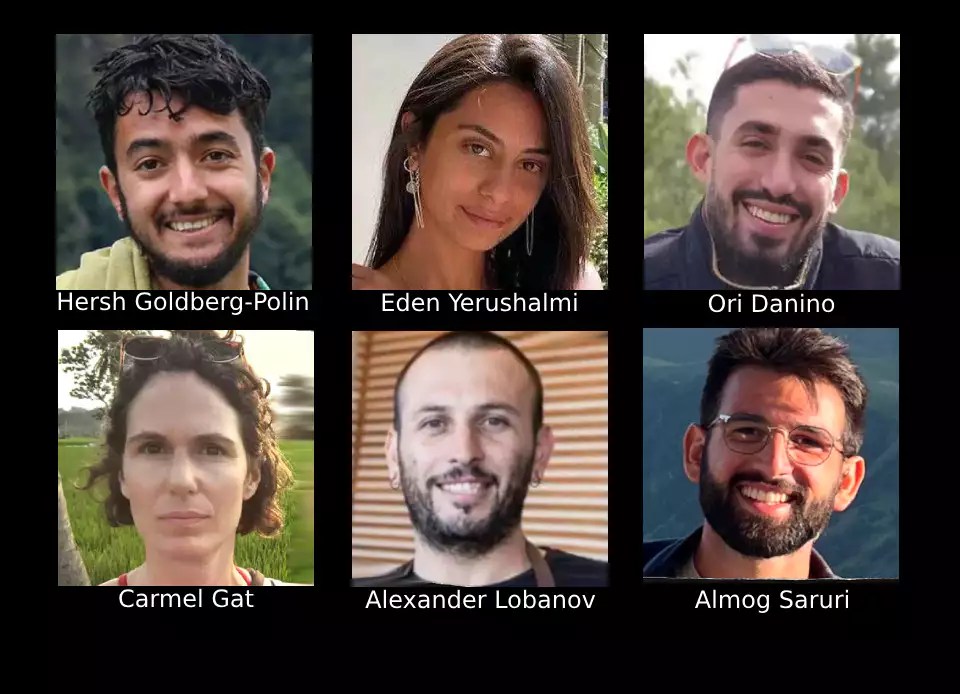
“Each and every blade of grass has a special song of its own.” – Naomi Shemer, based on Rebbe Nachman of Breslav
In the midst of the creation narrative, before humankind even enters the scene, parshat Bereishit offers a lesson about the power of faith and gratitude, one we have witnessed so vividly in each and every hostage who, thank God, has returned home.
In the retelling of creation in Bereishit, chapter 2, just before Adam is formed, the Torah states: “When no shrub of the field was yet on earth and no grasses of the field had yet sprouted, because God had not sent rain upon the earth and there were no human beings to till the soil.” Why did God withhold the rain? And why are two reasons given for why the vegetation had not grown? Rashi connects these two explanations: God withheld the rain because there were not yet human beings who could be makir tov (to appreciate the rain). Only once Adam sensed the world’s need for sustenance did he pray for rain, and it was that prayer that brought the grasses and trees to life.
Rashi’s insight highlights several key ideas. First, Adam prays not only for himself, but for the sake of the world. Second, tefilla cultivates within us the capacity to be makir tov — to feel and express gratitude to God and to others for the good we receive. Finally, the world itself reached its completion — the grasses only began to grow — when Adam prayed. Our very sustenance, and the flourishing of the world, depend on our tefillot.
This message finds powerful expression in the chatufim, who have shown almost superhuman strength, faith, and gratitude. With radiant smiles, wrapped in Israeli flags, and in their renewed embrace of mitzvot like tefillin and tefilla. Their example is not only a source of inspiration but also a wellspring of strength — one that will help us recreate, renew, and heal Israeli society. Shabbat Shalom – Karen Miller Jackson